What Causes the Difference Between Quiet and Explosive Eruptions Explain
Outside of the kitchen this means that the primary product of quiet eruptions is runny lava while the most explosive eruptions spew forth not only thicker lava but also rock fragments and noxious gases which can pummel down the sides of the volcano at speeds of. The differences are the kind of magma that the volcano has and how much gas is dissolved in the magma.

An Introduction To Volcanoes Ppt Download
What is the difference between quiet and explosive eruptions.
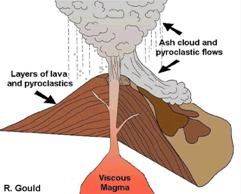
. Thats why cinder cone. An explosive eruption would be more likely to increase the steepness of a volcanic cone. In an explosive eruption the magma is high in silica which causes the magma to be thick and sticky.
The main factor that accounts for the difference between quiet and explosive volcanic eruptions is. However the effects of explosive eruptions can be incredibly destructive. Quiet eruption flows easeir cause it has a low viscosity and lava flows easier but explosive eruption has a high viscosity and lava flows slower What do explosive and quiet eruption have in common.
Volcanic eruptions may fall into six major types. The most common type of volcanic eruption occurs when magma the term for lava when it is below the Earths surface is released from a volcanic vent. Gasses may cause the eruption to be in a single vent a series of vents or along a crack in the earths crust.
Eruptions can be effusive where lava flows like a thick sticky liquid or explosive where fragmented lava explodes out of a vent. The main factor that accounts for the difference between quiet and explosive volcanic eruptions is. How magma composition affects the eruption of a volcano.
A volcano erupts explosively if its magma is high in silica. Some submarine volcanoes are phreatomagmatic if the magma is gas-rich for example Surtsey in Iceland. The silica content determines whether the magma is viscous or not.
What is the difference between an explosive and a quiet volcanic eruption. The material can also rise several kilometers into the air. The second phase of the Eyjafjallajökull eruption in 2010 was phreatomagmatic as a result of magma erupting under ice.
Icelandic Hawaiian Strombolian Vulcanian Pelean and Plinian. Volcanic eruptions are largely thought to occur when there is a huge pressure difference or gradient between the broiling magma within the chamber and the outside world. Explosive eruptions occur where cooler more viscous magmas such as andesite reach the surface.
D- the silica content of the magma. During an explosive eruption clouds of hot debris ash and gas rapidly shoot out from a volcano. Explosive Eruptions are much rarer than nonexplosive eruptions.
Volcanic eruptions may fall into six major types. There are generally two places where you f. What causes quiet and explosive eruptions.
The amount of water vapor and other gases present is one factor that determines whether a volcanic eruption will be quiet or explosive. Ash clouds Rabul 1994. What causes an eruption to be explosive.
T he difference between a quiet and explosive eruption is the silica content. In a quiet eruption the magma is low in silica allowing the magma to flow out gently. Outside of the kitchen this means that the primary product of quiet eruptions is runny lava while the most explosive eruptions spew forth not only thicker lava but also rock fragments and noxious gases which can pummel down the sides of the volcano at speeds of nearly 100 kilometers per hour about 60 miles per hour.
Instead of producing lava flows explosive eruptions cause molten rock to be blown into tiny particles that. Magmas differ in composition which affects viscosity. Lava flows are much more thick and sticky so do not flow downhill as easily.
In a quiet eruption the lava flows and spreads out over a large area. Before lava reaches the surface the molten material is called. Gas expands boils away as magma reaches surface causing an explosion.
In an explosive eruption the magma is high in silica which causes the magma to be thick and sticky. Phreatomagmatic eruptions are a type of explosive eruption that results from magma erupting through water. Explosive Volcanoes Has sticky lava high in silica which holds the gas in Gas cannot escape so pressure builds up Once the pressure is too great the top explodes ejecting rock fragments ash and lava into the air.
Explosive eruptions generally involve magma that is more viscous and has a higher gas content. In an explosive eruption pyroclastic material piles up much higher. Answer 1 of 3.
In a quiet eruption the magma is low in silica allowing the magma to flow out gently. Dissolved gases cannot escape as easily so pressure may build up until gas explosions blast rock and lava fragments into the air. D- the silica content of the magma.
Such magma is often shattered into pyroclastic fragments by explosive gas expansion during an eruption. The powerful eruptions cause material to travel faster than 350 meters per seconds or 800 mph. Icelandic Hawaiian Strombolian Vulcanian Pelean and Plinian.
The main hazard from a quiet volcanic eruption is. Explosive eruptions generally involve magma that is more viscous and has a higher gas contentSuch magma is often shattered into pyroclastic fragments by explosive gas expansion during an eruption. Earthquake activity due to the gasses forcing their way through cracks almost always signals when an eruption is going to occur.
The higher the pressure builds before eruption the greater the explosion. An explosive eruption is caused by viscous magma stiff or thick resists flow with a high gas content most of the gas is water. The presence of gas is the driving force for explosion.
In explosive eruptions the fragmented rock may be accompanied by ash and. Presumably you mean volcanic eruptions. Before lava reaches the surface the molten material is called.
The eruption occurs from the fragmentation and explosion of a volcanic conduit lava plug but also from the rupture of a lava dome. The eruption causes tephra ash clouds and pyroclastic flow. The main hazard from a quiet volcanic eruption is.

Geological Society Effusive Explosive Eruptions

Volcano Types 39 Volcanoes Are Either Explosive Of Non Explosive Ppt Video Online Download
0 Response to "What Causes the Difference Between Quiet and Explosive Eruptions Explain"
Post a Comment